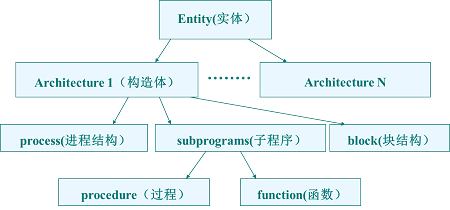
VHDL简介及其结构
VHDL的基本概念
VHDL-VHSIC Hardware Decription Language 其中VHSIC-Very High Speed Integrated Circuit 电子设计自动化的关键技术之一是要求用形式化方法来描述硬件系统。VHDL适应了这种要求。
Verilog HDL: 另一种硬件描述语言,由Verilog 公司开发,1995年成为IEEE标准。 优点:简单、易学易用 缺点:功能不如VHDL强大,仿真工具少 VHDL: 1987年成为IEEE标准 优点:功能强大、通用性强。 缺点:难学
VHDL的基本结构
系统设计的描述等级:行为级(模块)、RTL级(触发器)、逻辑门级(逻辑门)、版图级。
如何使用VHDL描述硬件实体:
library IEEE;
use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all;
use IEEE.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity count is
port ( clock,reset: in STD_LOGIC;
dataout: out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR (3 downto 0) );
end count;
architecture behaviorl of count is
signal databuffer: STD_LOGIC_VECTOR (3 downto 0);
begin
dataout<=databuffer;
process(clock,reset)
begin
if (reset='1') then databuffer<="0000";
elsif (clock'event and clock='1') then
if databuffer="1000" then
databuffer<="0000"; else databuffer<=databuffer+'1';
end if;
end if;
end process;
end behavioral;
1、entity(实体)
格式:
entity 实体名 is
[类属参数说明]
[端口说明]
end 实体名;
其中端口说明格式为:port(端口名1,端口名N:方向:类型)
其中方向有:in,out,inout,buffer,linkage
注意:in只能被引用,不能被赋值;out只能被赋值,不能被引用;buffer都可。
简单地说:in不可以出现在<=或:=的左边;out不可以出现在<=或:=的右边。
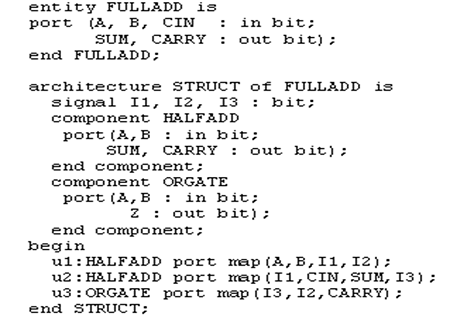
例子(HalfAdd)
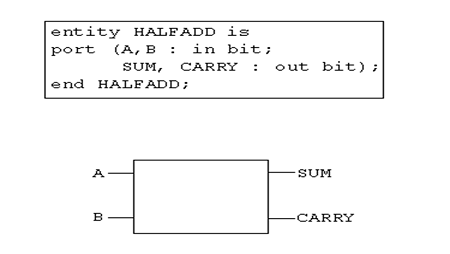
其内部结构将由Architecture来描述。
2、Architecture(构造体)
格式:
Arcthitecture 构造体名 of 实体名 is
[定义语句] 内部信号、常数、元件、数据类型、数等的定义
begin
[并行处理语句和block、process、function、procedure]
end 构造体名;

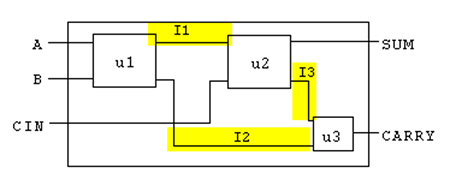
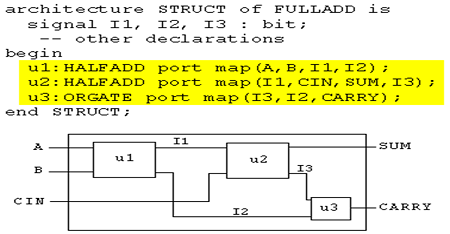
如何调用现有模块(全加器):

VHDL的设计初步
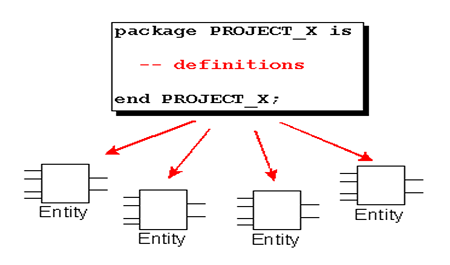
除了entity(实体)和architecture(构造体)外还有另外三个可以独立进行编译的设计单元:
(1)Package(包集合):属于库结构的一个层次,存放信号定义、常数定义、数据类型、元件语句、函数定义和过程定义。
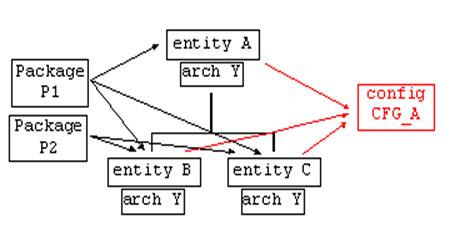
(2)Package Body:具有独立对端口(port)的package。
(3)Configuration(配置):描述层与层之间的连接关系以及实体与构造体之间关系。
库:数据的集合。内含各类包定义、实体、构造体等。
VHDL中的对象、操作符及数据类型
对象
对象:对客观实体的抽象和概括。VHDL中的对象有:
- Constant(常量),不可赋值
- Variable(变量),可被赋值(用“:=”),赋值后立即变化为新值。
- Signal(信号),可被赋值(用“<=”),赋值后不立即更新,当进程挂起后才开始更新。
对象的使用:
variable x,y:integer;--定义了整数型的变量对象x,y
constant Vcc:real;--定义了实数型的常量对象Vcc
signal clk,reset:bit;--定义了位类型的信号对clk,reset
注意:
1、variable只能定义在process和subprogram(包括function和procedure)中,不可定义在其外部。
2、signal不能定义在process和subprogram(包括function和procedure)中,只可定以在其外部。
对象的属性:例如,clk’event,表明clk信号的event属性。
常用属性:
- event:返回boolean值,信号发生变化时返回true
- last_value:返回信号发生此次变化前的值
- last_event:返回上一次信号发生变化到现在变化的间隔时间
- delayed[(时延值)]:使信号产生固定时间的延时并返回
- stable[(时延值)]:返回boolean, 信号在规定时间内没有变化返回true
- transaction:返回bit类型,信号每发生一次变化,返回值翻转一次
A<=B’delayed(10 ns); --B延时10ns后赋给A;
if(B’Stable(10 ns)); --判断B在10ns中是否发生变化
属性应用:信号的event和last_value属性经常用来确定信号的边沿。
--判断clk的上升沿
if ( (clk’event)and (clk=‘1’) and(clk’last_value=‘0’)) then
--判断clk的下降沿
if ( (clk’event)and (clk=‘0’) and(clk’last_value=‘1’)) then
VHDL的基本类型
1、bit(位): 0 和1
2、bit-Vector(位矢量): 例如:00110
3、Boolean “ ture”和“false”
4、time 例如:1 us、100 ms,3 s
5、character 例如:‘a’、’n’、’1’、 ’0’
6、string 例如:“sdfsd”、”my design”
7、integer 32位。例如:1、234、-2134234
8、real 范围-1.0E38~+1.0E38。例如:1.0、2.834、3.14、0.0
9、natural 自然数 和 positive 正整数
10、severity level(常和assert语句配合使用)包含有:note、warning、error、failure
以上十种类型是VHDL中的标准类型,在编程中可以直接使用。使用这十种以外的类型,需要自行定义或指明所引用的Library(库)和Package(包)集合。


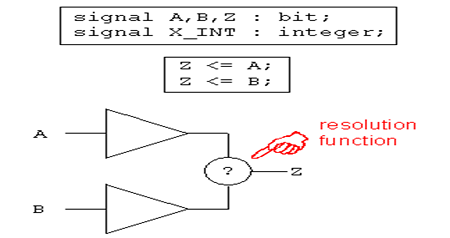
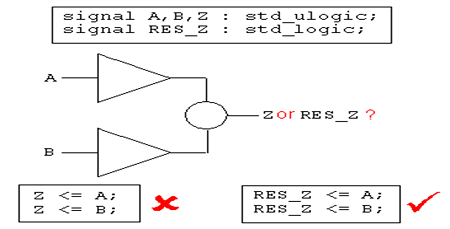
例子中信号Z有两个驱动A和B;Z必须定义为一种新的数据类型,否则Z将无法决定取值,语句视为非法。
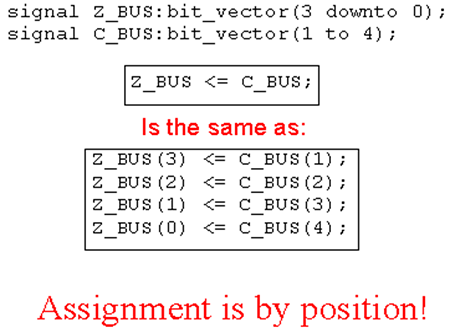

注意:赋值语句中的方向应和声明中的方向一样
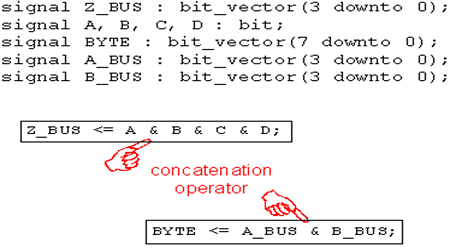
链接操作符,使用&
集合操作,使用()
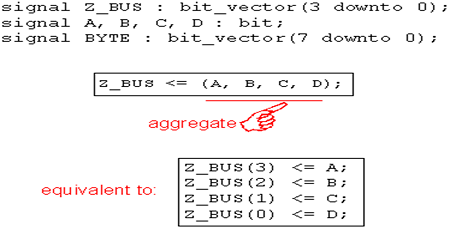
集合操作,采用序号

集合操作,采用others

如何在VHDL中定义类型、信号及赋值
通用格式:
type 类型名 is 数据类型定义
定义自己的数据类型:
1、枚举类型enumberated
type 数据类型名 is (元素,元素……);
type week is (sun,mon,tue,thu,fri,sat);
type std_logic is (‘1’,’0’,’x’,’z’);
2、整数型integer、实数型real
type 数据类型名 is 数据类型定义 约束范围;
type week is integer range 1 to 7;
type current is real range -1E4 to 1E4
3、数组类型array
type 数据类型名 is array 范围 of 元数据类型名;
type week is array (1 to 7) of integer;
type deweek is array (1 to 7) of week;
4、纪录类型record
type 数据类型名 is recoerd
元素名:数据类型名;
元素名:数据类型名;
···
end record;
例如:
type order is record
id:integer;
date:string;
security:boolean;
end record;
引用:signal flag:boolean;
signal order1:order;
order1<=(3423,”1999/07/07”,true);
flag<=order1.security;
5、时间类型time
type 数据类型名 is 范围
units 基本单位;
单位;
end units
type time is range -1E18 to 1E18
units
us;
ms=1000 us;
sec=1000 ms;
min=60 sec;
end units
注意:引用时间时,有的编译器要求量 与单位 之间应有一个空格如:1 ns;不能写为1ns;
6、文件类型file
7、存取类型access
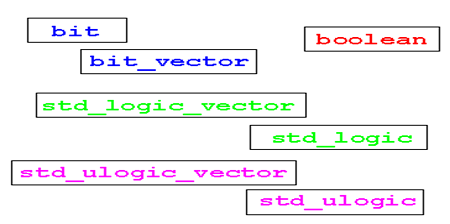
IEEE 1164中定义的类型
1、std_ulogic是对位(bit)类型的扩展,只允许一个驱动源。强驱动具有高可靠性、信号传输无延迟、驱动能力强等特点;弱驱动低电压。

2、std_logic同std_ulogic一样有九个状态,允许一个或多个驱动源。
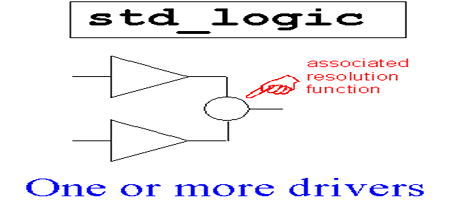
3、std_unlogic_vector和std_logic_vector

例子1(声明使用的库和包)

例子2(std_ulogic 和std_logic的区别)
VHDL中的操作符
操作符:
VHDL中的操作符应用要点
-
VHDL属于
强类型,不同类型之间不能进行运算和赋值,可以进行数据类型转换 -
vector
不表示number -
array
不表示number
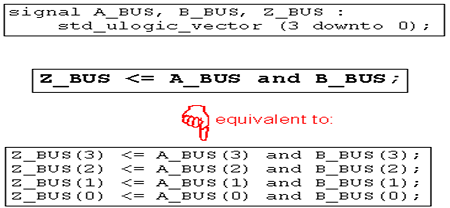
1、逻辑操作符
and、nand、or、nor、xor和not(优先级高)。
应用类型:
应用例子:
2、关系操作符
<、>、=、<=、>=、/=
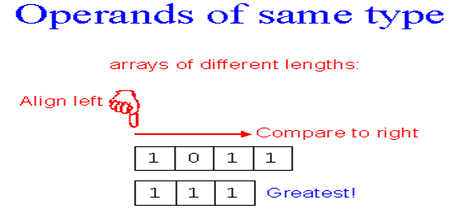
注意:ARRAY(数组)没有数字概念,数组“111”不等于7。
3、数学运算符
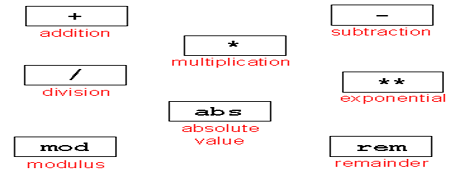
注意:上述运算符应用于 integer,real,time 类型,不能用于vector(如果希望用于vector,可以使用库IEEE的std_logic_unsigned包,它对算术运算符进行了扩展)。
VHDL中的控制语句及模块

Architecture中的语句及子模块之间是并行处理的- 子模块
block中的语句是并行处理的 - 子模块
process中的语句是顺序处理的 - 子模块
subprogram中的function和procedure是顺序处理的
Arcthitecture(构造体)的格式为:
Arcthitecture 构造体名 of 实体名 is
[定义语句] 内部信号、常数、元件、数据类型、函数等的定义
begin
[并行处理语句和block、process、function、procedure]
end 构造体名;
block的编写
Architecture中的Block。
一般Block:
块名:
BLOCK
[定义语句]
begin
[并行处理语句]
end block 块名
条件Block:
块名:
BLOCK [(布尔表达式)]
[定义语句]
begin
[并行处理语句]
[信号]<= guarded [信号,延时];
end block 块名
例子:
myblock1:
block(clk=‘1’)
signal:qin:bit:=‘0’;
begin
qout<= guarded qin;
end block myblock1
myblock2:
block
begin
qout<=qin;
end block myblock2
process的编写
[进程名:]
process [(触发信号列表)]
[定义语句;]
begin
[串行处理语句]
end process
exp1:
process (clk,qin)
variable:qin:bit:=‘0’;
begin
qout<=qin;
end process
exp2:
process
begin
wait on clk,qin;
qout<=qin;
end process
值的更新:
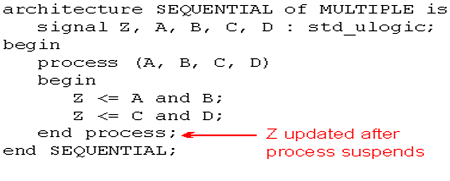
当A、B、C、D中任一信号发生变化时,进程将开始执行,当执行Z<=AandB后,Z的值不会立即变化;同理执行Z<=CandD后Z的值也不会立即变化。当执行end process后,Z的值才开始更新,同时系统挂起开始等待敏感信号。
process中敏感信号列表的普遍原则是:在process中,其值被引用的信号应当出现在敏感信号列表中。
例子:二选一的选择器:A、B为输入信号;SEL为选路信号;Z为输出信号。
MUX: process(A,B,SEL)
begin
if SEL = '1' then
Z <= A;
else
Z <= B;
end if;
end process MUX;
如下设计不符合要求:
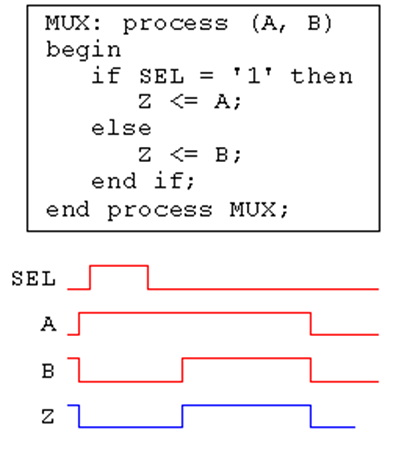
function和procedure的编写
procedure 过程名(参数1,参数2 …...)is
[定义语句]
begin
end 过程名
例子:
procedure max(a,b:in bit;
flag:out boolean)is
begin
if (a=b)then
flag<=true;
end if
end max;
VHDL中的流程控制语句的书写
Wait语句
wait语句使系统暂时挂起(等同于end process),此时,信号值开始更新。条件满足后,系统将继续运行。
wait; --无限等待
wait on [信号列表] --等待信号变化
wait until [条件]; --等待条件满足
wait for [时间值]; --等待时间到
process(a,b)
begin
y<=a and b;
end process
等效于:
process
begin
wait on a,b;
y<=a and b;
-- 错误 如果process中已有敏感信号进程中不能使用wait语句
process(a,b)
begin
wait on a,b;
y<=a and b;
end process
如果process中没有敏感信号列表,其进程中也没有wait语句,则process中的程序代码循环执行。
--功能:产生频率为100ns的clk信号。
process
begin
clk<=not clk after 50 ns ;
end process
assert语句
assert 条件 [report 输出信息] [severity]
条件为true 时执行下一条语句,为false 时输出错误信息和错误的严重级别。
...
assert(sum=100)report “sum /=100” severity error;
next statement
if语句
if 条件 then
[顺序执行语句]
[else]
[顺序执行语句]
end if
if 条件 then
[顺序执行语句]
[elsif]
[顺序执行语句]
[elsif]
[顺序执行语句]
...
[else]
end if
case语句
process(A,B,C,X)
begin
case X is
when 0 to 4 =>
Z <= B;
when 5 =>
Z <= C;
when 7 | 9 =>
Z <= A;
when others =>
Z <= 0;
end case;
end process;
for loop语句
循环变量不需要定义(声明);例子中 i 不需要定义。
for i in 1 to 10 loop
sum = sum+1;
end loop
用next跳出循环:
for i in 1 to 10 loop
sum=sum+1;
next when sum=100;
end loop
用exit结束循环:
for i in 1 to 10 loop
sum=sum+1;
exit when sum=100;
end loop
while语句
While i<10 loop
sum=sum+1;
i=i+1;
end loop
并行处理语句
信号赋值:符号“<=”进行信号赋值操作。注意用在并行处理语句中时,符号<=右边的值是此条语句的敏感信号,即符号<=右边的值发生变化就会重新激发此条赋值语句,也即符号<=右边的值不变化时,此条赋值语句就不会执行。如果符号<=右边是常数则赋值语句一直执行。
Myblock: Block
begin
clr<=‘1’ after 10 ns;
clr<=‘0’ after 20 ns;
end block myblock
上述程序执行10ns后clr为1,又过10ns后0赋给了clr,此时clr以前的值1并没有清掉,clr将出现不稳定状态。
process
begin
clr<=‘1’ after 10 ns;
clr<=‘0’ after 20 ns;
end block myblock
上述程序执行10ns后clr为1,又过20ns后clr的值变为0。
条件信号带入语句:
Block
begin
sel<=b & a;
q<=ain when sel=“00”
else bin when sel=“01”
else cin when sel=“10”
else din when sel=‘11”
else xx;
end block
选择信号带入语句:
Block
begin
with sel select
q<=ain when sel=“00”,
bin when sel=“01”,
cin when sel=“10”,
din when sel=‘11”
xx; when others;
end block
总结
1、顺序执行语句 wait、assert、if -else 、case、for-loop、while语句只能用在process、function和procedure中;
2、并行处理语句(条件信号带入和选择信号带入)只能用在architecture、block中;
状态机的设计
状态机是一类十分重要的时序电路,是许多数字电路的核心部件。
状态机的结构
1、组合逻辑部分(状态译码器和输出译码器)
2、寄存器部分
各部分功能:
(1)状态译码器:确定状态机的下一个状态。
(2)输出译码器:确定状态机输出。
(3)状态寄存器:存储状态机的内部状态。
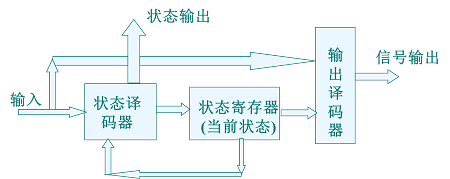
状态的转换:
下一个状态由译码器根据当前状态和输入条件决定。
输出信号的产生:
输出信号由译码器根据当前状态和输入条件决定。
状态机的时序
同步时序状态机:
由时钟信号触发状态的转换和信号的输出。
异步时序状态机:
状态的转移和输出不与时钟信号同步。
状态机设计
类型:
1、米里(mealy)状态机:使用输入信号
2、莫尔(moore)状态机:不使用输入信号
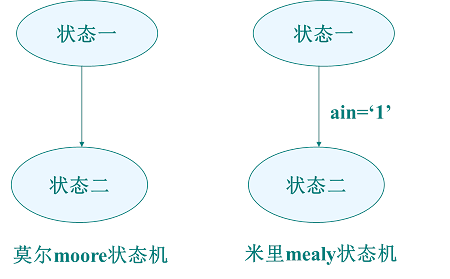
表达方式:状态图、状态表、流程图。