逻辑回归
优点:计算代价不高,易于理解实现
缺点:容易欠拟合,分类精度可能不高
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型数据
为了实现逻辑回归,我们在每个特征上乘以一个回归系数,然后把所有的结果值相加,将这个总和代入Sigmoid函数中,进而得到一个0-1范围之间的数值。任何大于0.5的分为1类,小于0.5归为0类。最佳回归系数多少?
这里将实现逻辑回归算法,并将之应用于两个数据集:Logistic_data1.txt和Logistic_data2.txt
需要实现的函数:
- plot_data: 绘制二维的分类数据
- sigmoid: sigmoid函数
- cost_function: 逻辑回归的代价函数
- predict: 逻辑回归的预测函数
- cost_function_reg: 逻辑回归带正则化项的代价函数
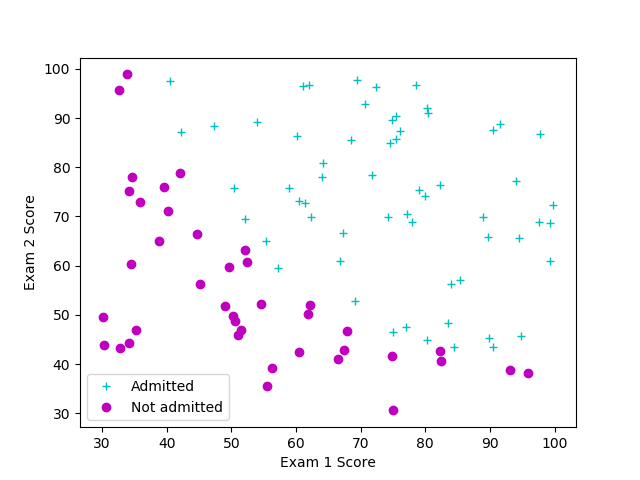
数据可视化
pos = y == 1
neg = y == 0
plt.plot(X[pos, 0], X[pos, 1], 'c+', label="Admitted")
plt.plot(X[neg, 0], X[neg, 1], 'mo', label="Not admitted")
sigmoid函数
逻辑回归的假设模型:
其中函数$g(·)$是sigmoid函数,定义为:
代价函数与梯度
现在需要实现逻辑函数回归的代价函数及其梯度。逻辑回归的代价函数为:
对应的梯度向量各分量为:
传入初始参数,cost_function的代价约为0.693。
使用fmin_cg学习模型参数
使用scipy.optimize.fmin_cg函数实现代价函数$J(\theta)$的优化,得到最佳参数$\theta^{*}$。
调用该函数的方法如下:
ret = op.fmin_cg(cost_function,
theta_initial,
fprime = cost_gradient,
args = (X,y),
maxiter = 200,
full_output = True)
其中cost_function为代价函数,theta_initial为需要优化的参数的初始值,fprime=cost_gradient给出了代价函数的梯度,args=(X,y)给出了需要优化的函数与对应的梯度计算所需要的其他参数,maxiter=400给出了最大迭代次数,full_output=True则指明该函数除了输出优化得到的参数theta_opt外,还会返回最小的代价函数值cost_min等内容。对一组参数得到的代价约为0.203(cost_min)。
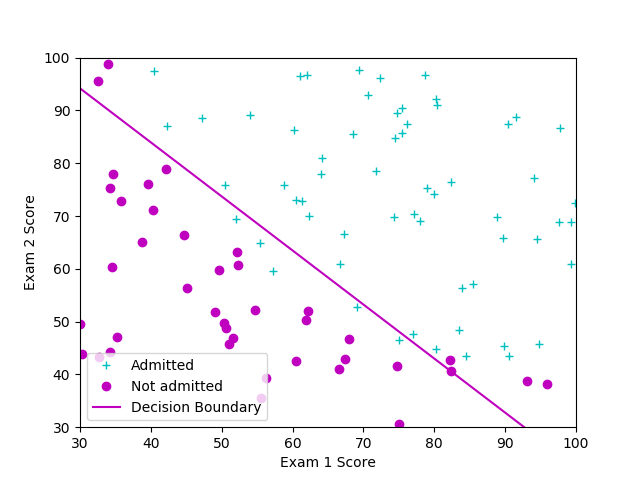
评估逻辑回归模型
在获得模型参数后,可以使用模型预测一个学生能够被大学录取的几率。如果某学生考试一的成绩为45,考试二的成绩为85,能够得到录取几率约为0.776。
predict函数输出”1”或”0”,通过计算分类正确的样本百分数,可以得正确率。
正则化的逻辑回归
调用函数plot_data可视化第二组数据。
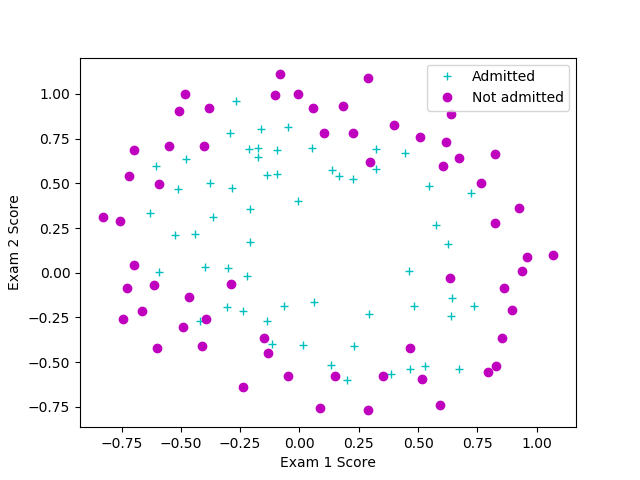
特征变换:
创建更多的特征是充分挖掘数据中的信息的一种有效手段。该函数map_feature中,将数据映射为6阶多项式的所有项。
逻辑回归的代价函数为:
对应的梯度向量各分量为:
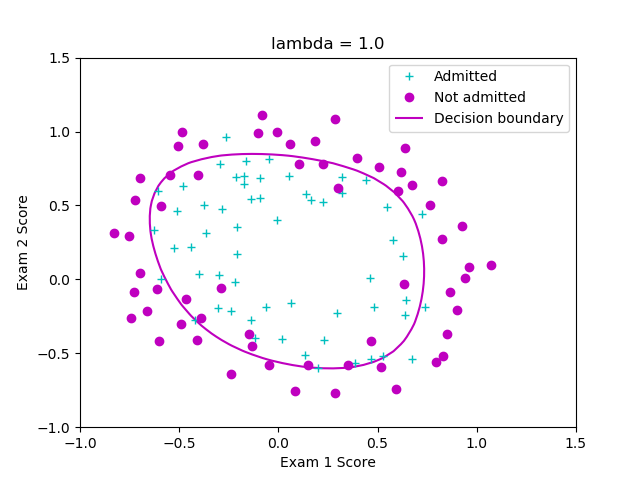
如果将参数 初始化为全零值,相应的代价函数约为0.693,。可以使用与前述无正则化项类似的方法实现梯度下降,获得优化后的参数$\theta^{*}$。
可以调用plot_decision_boundary函数来查看最终得到的分类面。建议你调整正则化项的系数,分析正则化对分类面的影响。
程序代码
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import scipy.optimize as op
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_data(X, y):
"""This function plots the data points X and y into a new figure.
It plots the data points with red + for the positive examples,
and blue o the negative examples. X is assumed to be a Mx2 matrix.
"""
plt.figure()
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
pos = y == 1
neg = y == 0
plt.plot(X[pos, 0], X[pos, 1], 'c+', label="Admitted")
plt.plot(X[neg, 0], X[neg, 1], 'mo', label="Not admitted")
# ============================================================
plt.xlabel("Exam 1 Score")
plt.ylabel("Exam 2 Score")
def plot_decision_boundary(theta, X, y):
"""绘制分类面。"""
plot_data(X[:, 1:], y)
_, d = X.shape
if d <= 3:
plot_x = np.array([np.min(X[:, 1])-2, np.max(X[:, 1])+2])
plot_y = -1.0/theta[2]*(theta[1]*plot_x + theta[0])
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y, 'm-', label="Decision Boundary")
plt.xlim([30, 100])
plt.ylim([30, 100])
else:
n_grid = 50
u = np.linspace(-1, 1.5, n_grid)
v = np.linspace(-1, 1.5, n_grid)
z = np.zeros((n_grid, n_grid))
for i in range(n_grid):
for j in range(n_grid):
uu, vv = np.array([u[i]]), np.array([v[j]])
z[i, j] = np.dot(map_feature(uu, vv), theta)
z = z.T
CS = plt.contour(u, v, z, lw=2, levels=[0.0], colors=['m'])
CS.collections[0].set_label('Decision boundary')
plt.legend()
def sigmoid(z):
"""Compute sigmoid function"""
z = np.asarray(z)
g = np.zeros_like(z)
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
g = 1.0/(1.0+np.exp(-z))
# ============================================================
return g
def cost_function(theta, X, y):
"""逻辑回归的代价函数,无正则项。"""
J = 0.0
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
m = 1.0*len(y)
J = (1/m)*np.sum(-np.dot(np.log(0.000001+sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))),y)-np.dot(np.log(0.000001+1-sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))),(1-y)))
# ============================================================
return J
def cost_gradient(theta, X, y):
"""逻辑回归的代价函数的梯度,无正则项。"""
m = 1.0*len(y)
grad = np.zeros_like(theta)
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
h_theta = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))
grad = np.dot(X.T, h_theta-y)/m
# ============================================================
return grad
def predict(theta, X):
"""Predict whether the label is 0 or 1
using learned logistic regression parameters theta.
"""
m, _ = X.shape
pred = np.zeros((m, 1), dtype=np.bool)
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
pred = 1/(1+np.exp(-np.dot(X, theta)))
# ============================================================
return pred
def map_feature(X1, X2, degree=6):
"""Feature mapping function to polynomial features."""
m = len(X1)
assert len(X1) == len(X2)
n = int((degree+2)*(degree+1)/2)
out = np.zeros((m, n))
idx = 0
for i in range(degree+1):
for j in range(i+1):
# print i-j, j, idx
out[:, idx] = np.power(X1, i-j)*np.power(X2, j)
idx += 1
return out
def cost_function_reg(theta, X, y, lmb):
"""逻辑回归的代价函数,有正则项。"""
m = 1.0*len(y)
J = 0
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
J = (1/m)*np.sum(-np.dot(np.log(0.000001+sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))),y)-np.dot(np.log(0.000001+1-sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))),(1-y)))+(lmb/(2*m))*np.sum(theta*theta)
# ============================================================
return J
def cost_gradient_reg(theta, X, y, lmb):
"""逻辑回归的代价函数的梯度,有正则项。"""
m = 1.0*len(y)
grad = np.zeros_like(theta)
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
h_theta = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))
grad = np.dot(X.T, h_theta-y)/m+(lmb/m)*theta
# ============================================================
return grad
def logistic_regression():
"""针对第一组数据建立逻辑回归模型。"""
# 加载数据
data = np.loadtxt("Logistic_data1.txt", delimiter=",")
X, y = data[:, :2], data[:, 2]
# 可视化数据
plot_data(X, y)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 计算代价与梯度
m, _ = X.shape
X = np.hstack((np.ones((m, 1)), X))
# 初始化参数
theta_initial = np.zeros_like(X[0])
# 测试 sigmoid 函数
z = np.array([-10.0, -5.0, 0.0, 5.0, 10.0])
g = sigmoid(z)
print("Value of sigmoid at [-10, -5, 0, 5, 10] are:\n", g)
# 计算并打印初始参数对应的代价与梯度
cost = cost_function(theta_initial, X, y)
grad = cost_gradient(theta_initial, X, y)
print("Cost at initial theta (zeros): ", cost)
print("Gradient at initial theta (zeros): \n", grad)
# 使用 scipy.optimize.fmin_cg 优化模型参数
args = (X, y)
maxiter = 200
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
ret = op.fmin_cg(cost_function,
theta_initial,
fprime = cost_gradient,
args = (X,y),
maxiter = 200,
full_output = True)
# ============================================================
theta_opt, cost_min, _, _, _ = ret
print("Cost at theta found by fmin_cg: ", cost_min)
print("theta: \n", theta_opt)
# 绘制分类面
plot_decision_boundary(theta_opt, X, y)
plt.show()
# 预测考试一得45分,考试二得85分的学生的录取概率
x_test = np.array([1, 45, 85.0])
prob = sigmoid(np.dot(theta_opt, x_test))
print("For a student with scores 45 and 85, we predict")
print("an admission probability of ", prob)
# 计算在训练集上的分类正确率
p = predict(theta_opt, X)
print("Train Accuracy: ", np.mean(p == y)*100)
def logistic_regression_reg(lmb=1.0):
"""针对第二组数据建立逻辑回归模型。"""
# 加载数据
data = np.loadtxt("Logistic_data2.txt", delimiter=",")
X, y = data[:, :2], data[:, 2]
# 可视化数据
plot_data(X, y)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 计算具有正则项的代价与梯度
# 注意map_feature会自动加入一列 1
X = map_feature(X[:, 0], X[:, 1])
# 初始化参数
theta_initial = np.zeros_like(X[0, :])
# 计算并打印初始参数对应的代价与梯度
cost = cost_function_reg(theta_initial, X, y, lmb=lmb)
grad = cost_gradient_reg(theta_initial, X, y, lmb=lmb)
print("Cost at initial theta (zeros): ", cost)
print("Gradient at initial theta (zeros): \n", grad)
# 使用 scipy.optimize.fmin_cg 优化模型参数
args = (X, y, lmb)
maxiter = 200
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
ret = op.fmin_cg(cost_function_reg,
theta_initial,
fprime = cost_gradient_reg,
args = (X,y,lmb),
maxiter = 200,
full_output = True)
# ============================================================
theta_opt, cost_min, _, _, _ = ret
print("Cost at theta found by fmin_cg: ", cost_min)
print("theta: \n", theta_opt)
# 绘制分类面
plot_decision_boundary(theta_opt, X, y)
plt.title("lambda = " + str(lmb))
plt.show()
# 计算在训练集上的分类正确率
pred = predict(theta_opt, X)
print("Train Accuracy: ", np.mean(pred == y)*100)
if "__main__" == __name__:
# 分别完成无正则项和有正则项的逻辑回归问题
logistic_regression()
# 可选:尝试不同正则化系数lmb = 0.0, 1.0, 10.0, 100.0对分类面的影响
logistic_regression_reg(lmb=1.0)