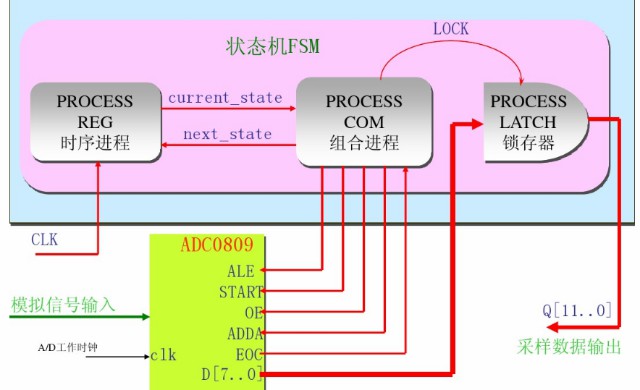
状态机设计:
(1)一组触发器的输出状态随着时钟和输入信号按照一定规律变化的一种机制或过程。
(2)一类十分重要的时序电路。
(3)许多数字电路的核心部件。
(4)任何时序电路都可以表示为有限状态机。
(5)状态的转换:下一个状态由译码器根据当前状态和输入条件决定。
(6)输出信号的产生:输出信号由译码器根据当前状态和输入条件决定。
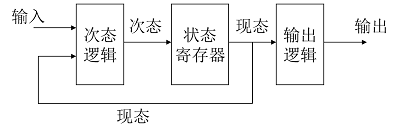
状态机的结构
组合逻辑部分
状态译码器(次态逻辑):确定状态机的下一个状态。
输出译码器(输出逻辑):确定状态机的输出。
寄存器部分
状态寄存器(内部状态):存储状态机的内部状态下一个状态不仅与输入信号有关,而且还与该寄存器的当前状态有关。
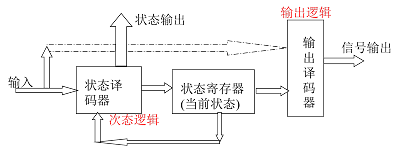
同步时序状态机:由时钟信号触发状态的转换和信号的输出。大多数可综合的状态机设计要求使用同步状态机。
异步时序状态机:状态的转移和输出不与时钟信号同步。
分类:
结构上:单进程状态机和多进程状态机。
编码方式:顺序编码、一维热码、其他编码。
输出的产生:Moore型、Mealy型。
状态机的设计
四部分:
(1)说明部分
状态名定义:用type语句定义数据类型,元素为枚举型。
状态变量:定义为信号,便于信息传递。
(2)主控时序进程
负责状态机的运转,时钟驱动下负责状态转换。
(3)主控组合进程
根据外部控制信号和当前状态值,确定下一个状态。
根据对内、外输出控制信号的内容。
(4)辅助进程:配合状态机工作的组合进程或时序进程。

--双进程状态机
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
ENTITY state_machine IS
PORT(reset, clk, x : IN STD_LOGIC;
z : OUT STD_LOGIC);
END state_machine;
ARCHITECTURE beh OF state_machine IS
type statetype is (state0, state1);
signal state, next_state: statetype := state0;
BEGIN
comb_process: process(state, x)
begin
-- describtion here
end process comb_process;
clk_process: process(clk)
begin
-- describtion here
end process clk_process;
END beh;
组合逻辑部分:下一状态与输出的计算。
comb_process: process (state, x)
Begin
case state is
when state0 =>
if x = ‘0’ then
next_state <= state1; z <= ‘1’;
else
next_state <= state0; z <= ‘0’;
end if;
when state1 =>
if x = ‘1’ then
next_state <= state0;z <= ‘0’;
else
next_state <= state1;z <= ‘1’;
end if;
end case;
end process comb_process;
Clock进程:采用一个同步复位来将状态机初始化到一个已知的状态。
clk_process: process(clk)
begin
wait until (clk’event and clk = ‘1’); -- wait until the rising edge
if reset = ‘1’ then -- check for reset and initialize state
state <= statetype'left;
else
state <= next_state;
end if;
end process clk_process;
end behavioral;
Moore型状态机的设计
Mooer状态机的输出只与当前的状态有关,也就是当前的状态决定输出,而与此时的输入无关,输入只决定状态机的状态改变,不影响电路最终的输出。
以存储控制器状态机的设计为例:
要求:
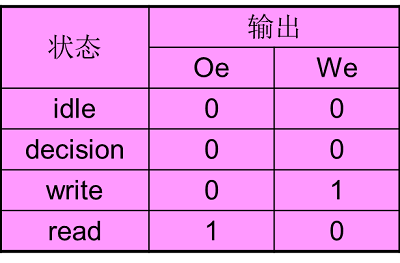
根据微处理器的读、写周期,分别对存储器输出两种信号
写使能:We
读使能:Oe
工作过程:
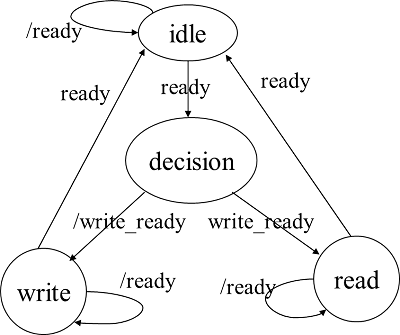
存储控制器的输入信号:
就绪:ready
读写:read_write
上电复位或ready有效
存储控制器开始工作,并在下一个时钟周期判断read_write信号,决定下次作业是读(Oe有效)还是写(We有效)
ready有效;
本次作业处理完成,恢复初始状态。
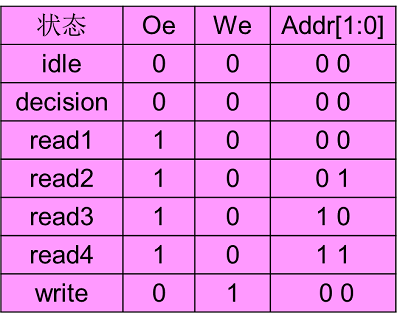
存储控制器各状态输出:
状态转移图:
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
ENTITY state_machine IS
PORT(reset, clk, x : IN STD_LOGIC;
z : OUT STD_LOGIC);
END state_machine;
ARCHITECTURE beh OF state_machine IS
type statetype is (idle, decision, read, write);
signal present_state, next_state: statetype := idle;
BEGIN
comb_process: process(present_state, x)
---
clk_process: process(clk)
---
END beh;
组合逻辑部分:
comb_process: process (present_state, read_write, ready)
Begin
case present_state is
when idle => oe<=<'0'; we<=<'0';
if ready ='1' then
next_state <= decision;
else
next_state <= idle;
end if;
when decision => oe<='0'; we<='0';
if read_write = '1' then
next_state <= read;
else
next_state <= write;
end if;
when read => oe=<'1'; we=<'0';
if ready ='1' then
next_state <= idle;
else
next_state <= read;
end if;
when write => oe=<'0'; we=<'1';
if ready ='1' then
next_state <= idle;
else
next_state <= write;
end if;
end case;
end process comb_process;
Clock进程:
clk_process: process(clk)
begin
wait until (clk’event and clk = ‘1’); -- wait until the rising edge
if reset = ‘1’ then -- check for reset and initialize state
present_state <= statetype’left;
else
present_state <= next_state;
end if;
end process clk_process;
状态机复位:
以SRAM存储控制器为例。使用时,首先输出总线标识F3(hex),在下一周期输出读写信号, read_write信号高电平。
读SRAM:
burst信号为低,单字节读
burst信号为高,4字节猝发
在连续读期间Oe有效,地址线依次递增,以便使SRAM输出地址连续,并能依次读四个连续地址内的数据
写SRAM:
单字节方式,写信号We有效时将数据写入到SRAM指定地址。
ready信号有效时,标志读、写操作完成。
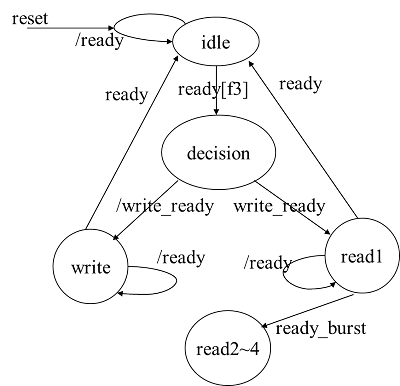
SRAM存储控制器,需要复位信号reset,需随时判断该信号是否有效。
方案一:
comb_process: process (reset, present_state, burst, read_write, ready)
Begin
if (reset='1') then
--由于隐含存储效应(保持原来的值),需指定复位值。
oe<='0'; we<='0'; addr<='00';
next_state=idle;
else
case present_state is
--
end case;
end if;
end process comb_process;
方案二:
comb_process: process (reset, present_state, burst, read_write, ready)
Begin
case present_state is
--
end case;
if (reset='1') then
--由于隐含存储效应,需指定复位值
next_state=idle;
oe<='0'; we<='0'; addr<='00';
end if;
end process comb_process;
SRAM存储控制器的同步复位双进程状态机:
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
ENTITY memory_controller IS
PORT(reset, read_write, ready, burst, clk: IN STD_LOGIC;
bus_id : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(7 DOWNTO 0);
Oe, We : OUT STD_LOGIC;
addr : OUT STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(1 DOWNTO 0));
END memory_controller;
ARCHITECTURE beh OF memory_controller IS
type statetype is (idle, decision, read1, read2, read3, read4, write);
signal present_state, next_state: statetype := idle;
BEGIN
comb_process: process(reset, bus_id, present_state, burst, read_write, ready)
---
clk_process: process(clk)
---
END beh;
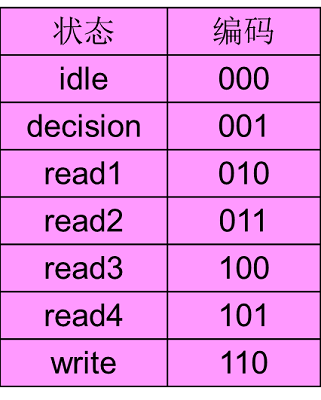
组合逻辑部分:
comb_process: process(reset, bus_id, present_state, burst, read_write, ready)
Begin
if (reset='1') then
oe<='0'; we<='0'; addr<='00';
next_state=idle;
else
case present_state is
when idle => oe<='0';we<='0';addr<="00";
if bus_id ="11110011" then
next_state <= decision;
else
next_state <= idle;
end if;
when decision => oe<='0'; we<='0';addr<="00";
if read_write = '1' then
next_state <= read1;
else
next_state <= write;
end if;
when read1 => oe<='1'; we<='0';addr<="00";
if ready ='0' then
next_state <= read1;
elsif burst='0' then
next_state=idle;
else
next_state <= read2;
end if;
when read2 => oe<='1'; we<='0';addr<="01";
if ready ='0' then
next_state <= read2;
else
next_state <= read3;
end if;
when read3 => oe<='1'; we<='0';addr<="10";
if ready ='0' then
next_state <= read3;
else
next_state <= read4;
end if;
when read4 => oe<='1'; we<='0';addr<="11";
if ready ='0' then
next_state <= read4;
else
next_state <= idle;
end if;
when write => oe<='0'; we<='1';addr<="00";
if ready ='1' then
next_state <= idle;
else
next_state <= write;
end if;
end case;
end process comb_process;
Clock进程(触发器实现):
clk_process: process(clk)
begin
if (clk'event and clk = '1') then
present_state <= next_state;
-- 下一状态时钟同步赋值
end if;
end process clk_process;
异步复位适用于上电复位,系统错误复位,占用资源较多。
clk_process: process(clk, reset)
begin
if reset = '1' then -- check for reset and initialize state
present_state <= idle;
elsif (clk'event and clk = '1') then
present_state <= next_state;
end if;
end process clk_process;
单进程状态机设计:
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
ENTITY memory_controller IS
PORT(reset, read_write, ready, burst, clk: IN STD_LOGIC;
bus_id : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(7 DOWNTO 0);
Oe, We : OUT STD_LOGIC;
addr : OUT STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(1 DOWNTO 0));
END memory_controller;
ARCHITECTURE beh OF memory_controller IS
type statetype is (idle, decision, read1, read2, read3, read4, write);
signal state: statetype;
BEGIN
state_tr: process(reset, clk)
---
END beh;
state_tr: process(reset, clk)
Begin
if (reset='1') then
state=idle;
elsif (clk'event and clk = '1') then
case state is
when idle =>
if bus_id ="11110011" then
state <= decision;
else
state <= idle;
end if;
when decision =>
if read_write = '1' then
state <= read1;
else
state <= write;
end if;
when read1 =>
if ready ='0' then
state <= read1;
elsif burst='0' then
state=idle;
else
state <= read2;
end if;
when read2 =>
if ready ='0' then
state <= read2;
else
state <= read3;
end if;
when read3 =>
if ready ='0' then
state <= read3;
else
state <= read4;
end if;
when read4 =>
if ready ='0' then
state <= read4;
else
state <= idle;
end if;
when write =>
if ready ='1' then
state <= idle;
else
state <= write;
end if;
end case;
end if;
end process state_tr;
with state select
oe=<='1' when read1|read2|read3|read4,
'0' when others;
with state select
we=<'1' when write,
'0' when others;
with state select
addr<="01" when read2,
"10" when read3,
"11" when read4,
"00" when others;
end beh;
moore型状态机的状态编码和信号输出方法:
顺序编码(符号化)
组合译码输出
并行译码输出
状态直接编码输出
一位有效编码方式
顺序编码:方式最简单,触发器数量最少,非法状态最少,容错技术最简单。但增加了状态之间转换的译码组合逻辑。输出的控制信号,如Oe、We等还需要一个组合进程作为控制译码器。
组合译码输出:oe、we、addr由状态位译码得到,多经过一级逻辑,在时钟上升沿之后才能到达输出端口,因此延迟较大
with state select
oe=<='1' when read1|read2|read3|read4,
'0' when others;
with state select
we=<'1' when write,
'0' when others;
with state select
addr<="01" when read2,
"10" when read3,
"11" when read4,
"00" when others;
并行译码输出:增加了一个输出寄存器,缩短了延迟,占用了资源。
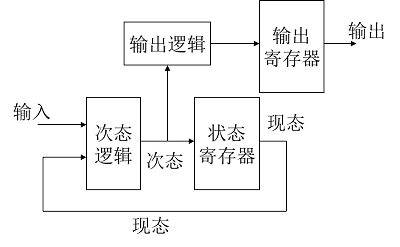
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
ENTITY memory_controller IS
PORT(reset, read_write, ready, burst, clk: IN STD_LOGIC;
bus_id : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(7 DOWNTO 0);
Oe, We : OUT STD_LOGIC;
addr : OUT STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(1 DOWNTO 0));
END memory_controller;
ARCHITECTURE beh OF memory_controller IS
type statetype is (idle, decision, read1, read2, read3, read4, write);
signal present_state, next_state: statetype;
signal addr_d: std_logic_vector(1 downto 0); -- 新增信号
BEGIN
state_comb: process(reset, bus_id, present_state, burst, read_write, ready)
with next_state select
addr_d<="01" when read2,
"10" when read3,
"11" when read4,
"00" when others;
clk_process: process(clk, reset)
END beh;
组合逻辑部分:
comb_process: process(reset, bus_id, present_state, burst, read_write, ready)
Begin
case present_state is
when idle => oe<='0'; we<='0';
if bus_id ="11110011" then
next_state <= decision;
else
next_state <= idle;
end if;
when decision => oe<='0'; we<='0';
if read_write = '1' then
next_state <= read1;
else
next_state <= write;
end if;
when read1 => oe<='1'; we<='0';
if ready ='0' then next_state <= read1;
elsif burst='0' then next_state=idle;
else next_state <= read2;
end if;
when read2 => oe<='1'; we<='0';
if ready ='0' then next_state <= read2;
else next_state <= read3;
end if;
when read3 => oe<='1'; we<='0';
if ready ='0' then next_state <= read3;
else next_state <= read4;
end if;
when read4 => oe<='1'; we<='0';
if ready ='0' then next_state <= read4;
else next_state <= idle;
end if;
when write => oe<='0'; we<='1';
if ready ='1' then next_state <= idle;
else next_state <= write;
end if;
end case;
end process comb_process;
Clock进程:
clk_process: process(clk, reset)
begin
if reset='1' then
present_state<=idle;
addr<="00";
elsif (clk'event and clk = '1') then
addr<=addr_d;
present_state <= next_state;
end if;
end process clk_process;
状态直接编码输出:
3位、7态编码 -> 5位、7态编码
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
ENTITY memory_controller IS
PORT(reset, read_write, ready, burst, clk: IN STD_LOGIC;
bus_id : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(7 DOWNTO 0);
Oe, We : OUT STD_LOGIC;
addr : OUT STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(1 DOWNTO 0));
END memory_controller;
ARCHITECTURE beh OF memory_controller IS
signal state: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0);
constant idle: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0) := "00000" ;
constant decision: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0) := "00001" ;
constant read1: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0) := "00100" ;
constant read2: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0) := "01100" ;
constant read3: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0) := "10100" ;
constant read4: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0) := "11100" ;
constant write: std_logic_vector(4 downto 0) := "00010" ;
BEGIN
state_rt: process(reset, clk)
---
end process state_rt;
we<=state(1);
oe<=state(2);
addr<=state(4 downto 3);
END beh;
state_tr: process(reset, clk)
Begin
if (reset='1') then
state=idle;
elsif (clk'event and clk = '1') then
case state is
when idle =>if bus_id ="11110011" then state <= decision;
else state <= idle;
end if;
when decision =>if read_write = '1' then state <= read1;
else state <= write;
end if;
when read1 =>if ready ='0' then state <= read1;
elsif burst='0' then state=idle;
else state <= read2;
end if;
when read2 =>if ready ='0' then state <= read2;
else state <= read3;
end if;
when read3 =>if ready ='0' then state <= read3;
else state <= read4;
end if;
when read4 =>if ready ='0' then state <= read4;
else state <= idle;
end if;
when write =>if ready ='1' then state <= idle;
else state <= write;
end if;
when others =>state <= write;
end case;
end if;
end process state_tr;
一位有效编码方式:用N个触发器来表示具有N个状态的状态机,每个触发器表示一种状态。大大简化了状态译码逻辑,提高了转换速度。不依赖于时钟的同步,属于异步时序的概念。
Mealy型状态机
输出是现态和输入信号的函数。一旦输入信号或状态发生变化,输出信号即刻变化,因此与Moore型状态机相比,Mealy型状态机的输出变化要领先一个周期。
其VHDL结构要求至少两个进程,或一个状态进程加一个独立的并行赋值语句。
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
ENTITY mealy_controller IS
PORT(clk, datain, reset: IN STD_LOGIC;
q : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(4 DOWNTO 0));
END mealy;
ARCHITECTURE beh OF mealy IS
type states is (st0, st1, st2, st3, st4);
signal stx : states;
signal q1 : STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(4 DOWNTO 0);
begin
comreg : process(clk, reset) -- 决定状态转换的进程
---
end process comreg;
com1 : process(stx, datain, clk) -- 输出控制信号的进程
---
end process com1;
q<=q1;
END beh;
决定状态转换的进程:
comreg : process(clk, reset)
Begin
if reset='1' then stx<=st0;
elsif clk'event and clk='1' then
case stx is
when st0 => if datain ='1' then stx <= st1; end if;
when st1 => if datain ='0' then stx <= st2; end if;
when st2 => if datain ='1' then stx <= st3; end if;
when st3 => if datain ='0' then stx <= st4; end if;
when st4 => if datain ='1' then stx <= st0; end if;
when others => stx <= st0;
end case;
end if;
end process comreg;
输出控制信号的进程
com1 : process(stx, datain, clk)
variable q2 : STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(4 DOWNTO 0);
Begin
case stx is
when st0 => if datain ='1' then q2 <= "10000"; else q2 <= "01010"; end if;
when st1 => if datain ='0' then q2 <= "10111"; else q2 <= "10100"; end if; when st2 => if datain ='1' then q2 <= "10101"; else q2 <= "10011"; end if; when st3 => if datain ='0' then q2 <= "11011"; else q2 <= "01001"; end if; when st4 => if datain ='1' then q2 <= "11101"; else q2 <= "01101"; end if;
when others => q2 <= "00000";
end case;
if clk'event and clk='1' then q1<=q2; end if;
-- 输出对应该时刻的状态,而非下一状态
end process com1;
状态机的容错设计
设状态位的数目为n,触发器数目为k,则k=[log2(n)]。如n=7,则k=3,有一种状态未定义。非法状态会影响逻辑设计、资源占用、稳定性。
不可避免会出现剩余状态,即未定义的编码组合。必须处理剩余状态,以避免系统的不稳定。处理剩余状态会耗用系统资源。处理方法:
(1)对每个状态明确处理
--转入空闲
case present_state is
when undefined=>next_state<=idle;
end case
--若有多个非法状态,转入其他任务,不作处理
case present_state is
when others=>next_state<=write;
-- "xxx"不处理
end case
一段式状态机
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity statmach is
port(
clk:in bit;
input:in bit;
reset:in bit;
output:out bit
);
end statmach;
architecture a of statmach is
type state_type is(s0,s1);
signal state:state_type;
begin
process(clk,reset)
begin
if reset='1'then
state<=s0;
elsif(clk'event and clk='1')then
case state is
when s0=>
state<=s1;
output<='0';
when s1=>
if input='1'then
state<=s0;
else
state<=s1;
end if;
output<='1';
end case;
end if;
end process;
end a;
Moore二段式
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity statmach is
port(
clock,s1,s2,reset:in std_logic;
r1,y1,g1,r2,y2,g2:out std_logic);
end statmach;
architecture exemplar of statmach is
type state_t is(st0,st1,st2,st3,st4,st5,st6,st7);
signal state,nxstate:state_t;
begin
process(reset,clock)
begin
if(reset='1')then
state<=st0;
elsif(clock'event and clock='1')then
state<=nxstate;
end if;
end process;
process(state,s1,s2)
begin
r1<='0';
y1<='0';
g1<='0';
r2<='0';
y2<='0';
g2<='0';
case state is
when st0=>
g1<='1';
r2<='1';
if s2=s1 then
nxstate<=st1;
elsif(s1='0' and s2='1')then
nxstate<=st2;
else
nxstate<=st0;
end if;
when st1=>
g1<='1';
r2<='1';
nxstate<=st2;
when st2=>
g1<='1';
r2<='1';
nxstate<=st3;
when st3=>
y1<='1';
r2<='1';
nxstate<=st4;
when st4=>
r1<='1';
g2<='1';
if(s1='0' and s2='0')then
nxstate<=st5;
elsif(s1='1' and s2='0')then
nxstate<=st6;
else
nxstate<=st4;
end if;
when st5=>
r1<='1';
g2<='1';
nxstate<=st6;
when st6=>
r1<='1';
g2<='1';
nxstate<=st7;
when st7=>
r1<='1';
y2<='1';
nxstate<=st0;
end case;
end process;
end exemplar;
Mealy型二段式
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity stmch1 is
port(clk,in1,rst:in std_logic;
out1:out std_logic);
end stmch1;
architecture behave of stmch1 is
type state_values is(sx,s0,s1);
signal state,next_state:state_values;
begin
process(clk,rst)
begin
if rst='1'then
state<=s0;
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
state<next_state;
end if;
end process;
process(state,in1)
begin
out1<='0';
next_state<=sx;
case state is
when s0=>
if in1='0' then
out1<='1';
next_state<=s1;
else
out1<='0';
next_state<=s0;
end if;
when s1=>
if in1='0' then
out1<='0';
next_state<=s0;
else
out1<='1';
next_state<=s1;
end if;
when sx=>
next_state<=sx;
end case;
end process;
end behave;
三段式
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity moore is
port(
rst;in std_logic;
clk:in std_logic;
x:in std_logic;
z:out std_logic;
);
end moore;
architecture behave of moore is
type state_type is(s0,s1,s2,s3);
signal current_state,next_state:state_type;
begin
STNCH:process --状态寄存器进程
begin
wait until clk'event and clk='1';
if rst='1' then
current_state<=s1;
else
current_state<=next_state;
end if;
end process;
STATE_TRANS:process(current_state,x)--次态逻辑
begin
next_state<=current_state;
case current_state is
when s0=>
if x='0' then
next_state<=s0;
else
next_state<=s2;
end if;
when s1=>
if x='0' then
next_state<=s0;
else
next_state<=s2;
end if;
when s2=>
if x='0' then
next_state<=s2;
else
next_state<=s3;
end if;
when s3=>
if x='0' then
next_state<=s3;
else
next_state<=s1;
end if;
end case;
end process;
OUT:process(current_state,x) --输出逻辑进程
begin
z<='0';
case current_state is
when s0=>
z<='0';
when s1=>
z<='1';
when s2=>
z<='1';
when s3=>
z<='0';
end case;
end process;
end behave;
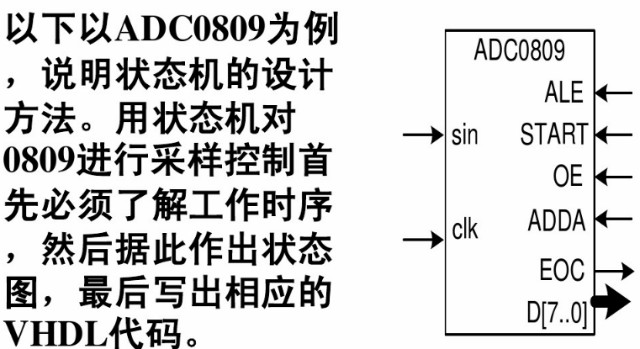
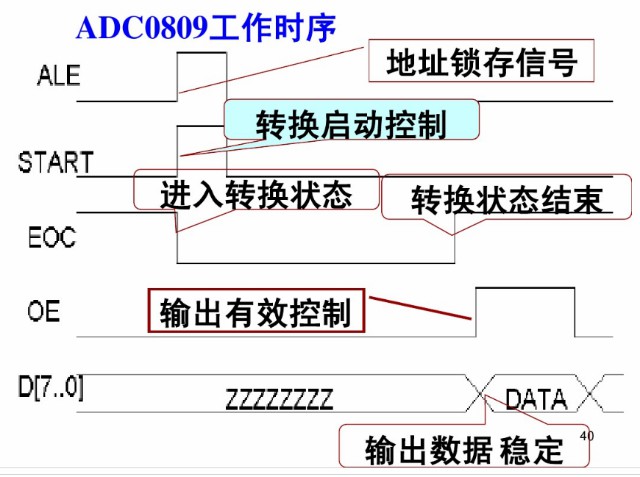
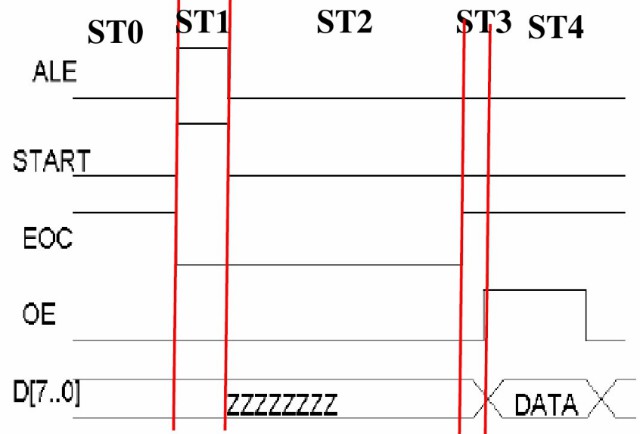
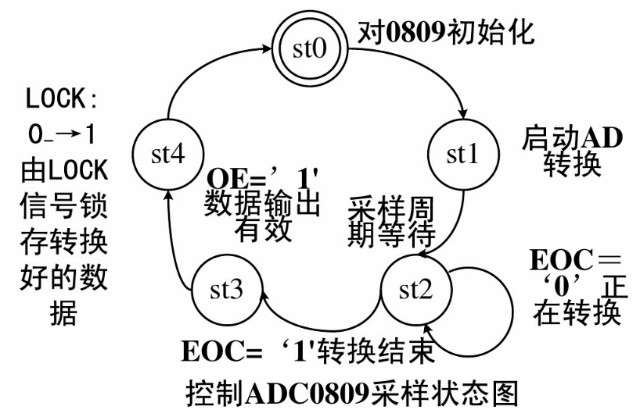
AD0809状态设计